Application
Contact Us
Phone
Address
No. 60, Yungjing East Road, Liyuan Town, Tongzhou District, Beijing City, China
Hydrogenation Process
Category:
Application
Hydrogenation is a chemical process where hydrogen (H₂) reacts with organic compounds in the presence of a catalyst. This process is typically conducted under high temperatures (100–400°C) and high pressures (1–30 MPa) to facilitate the bonding of hydrogen atoms with target molecules. Key objectives include the reduction of unsaturated bonds (e.g., alkenes, nitro compounds), removal of heteroatoms (sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen), or enhancement of product properties (e.g., fuel stability). Common applications include:
● Petroleum Refining: Hydrodesulfurization (HDS), hydrocracking.
● Chemical & Pharmaceutical Industries: Synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates, reduction of fine chemicals.
● New Energy Materials: Hydrogen energy storage and organic liquid hydrogen storage technologies.
Technology Trends
In the design and manufacturing of hydrogenation reactors, numerous challenges must be addressed, such as hydrogen infiltration into metal lattices under high temperature and pressure, leading to material embrittlement and cracking. Additionally, long-term gas-tight sealing under high pressure is critical to prevent hydrogen leakage and potential explosions.
New continuous flow reaction equipment (e.g., microchannel reactors, tubular reactors) is gradually replacing traditional batch reactors. Key advantages include:
● High specific surface area enhances mass/heat transfer rates, reducing reaction time from hours to minutes and improving product selectivity.
● Small reaction volume (milliliter-scale) minimizes hydrogen storage requirements and explosion risks.
● Modular design reduces equipment footprint, while catalyst online regeneration technology lowers consumption.
● Precise feeding reduces waste generation, aligning with green chemistry principles.
Case
PMG assisted a client in developing a skid-mounted continuous reaction system for hydrogenation processes. The workflow includes:
● Mixing & Reaction: Liquid feedstock from the raw material mixing tank is thoroughly blended with hydrogen before entering the reactor, where the reaction proceeds under controlled conditions (temperature, pressure) with catalyst participation.
● Gas-Liquid Separation: The product stream passes through a gas-liquid separation system to split into gaseous and liquid phases.
● Hydrogen Recycling: Separated hydrogen is recompressed, mixed with fresh hydrogen, and reused.
● Liquid Processing: The liquid phase undergoes atmospheric-pressure ammonia stripping, followed by distillation.
● Ammonia Recovery: Evaporated ammonia is compressed and recovered into a liquid ammonia tank for liquid feedstock preparation.
● Compact Design: The entire skid-mounted system occupies a footprint of 4m × 3m × 4m (L × W × H), enabling efficient space utilization.
This integrated solution enhances process safety, reduces hydrogen consumption, and supports closed-loop resource recovery.
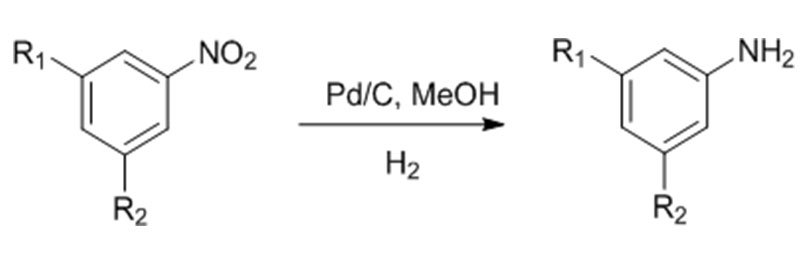
Reaction Equation
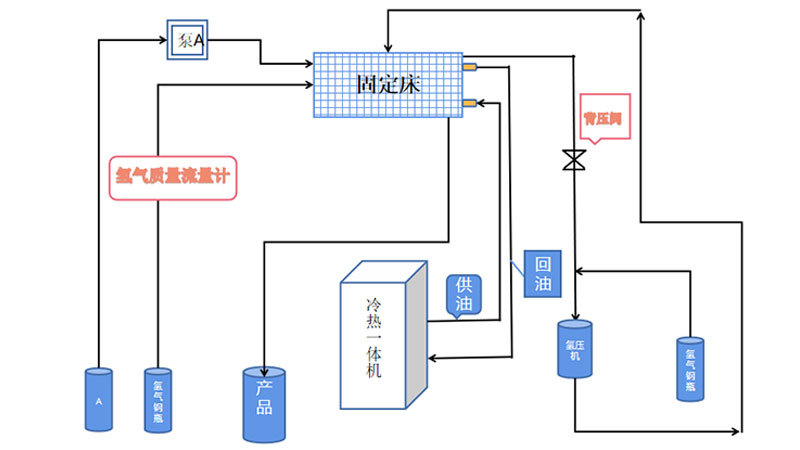
Industrial Production Process

Automatic Hydrogenation Reactor
Previous page
Next page
Other News

