Application
Contact Us
Phone
Address
No. 60, Yungjing East Road, Liyuan Town, Tongzhou District, Beijing City, China
Chlorination
Category:
Application
Chlorination refers to the chemical reaction of introducing chlorine atoms into the molecules of compounds. The process involving chlorination is known as chlorination technology, which primarily encompasses various types such as substitution chlorination, addition chlorination, and oxychlorination. As a fundamental reaction type in chemical production, chlorination plays a crucial role in numerous manufacturing fields. Below is a detailed introduction to the applications of chlorination in different industrial sectors:
Chemical Industry: In the chemical industry, chlorination is the core process for producing alkanes, chlorinated hydrocarbons, aluminum chloride, and other basic chemicals. Additionally, it is widely applied in the production of organic solvents, dyes, and pesticides. These chemicals have extensive applications in daily life and industrial production, and advancements in chlorination have directly driven the technological development of the chemical industry.
Petroleum Industry: The petroleum industry also relies heavily on chlorination. Through chlorination treatment, crude oil can be purified and its quality enhanced. Simultaneously, chlorination can adjust the properties of petroleum products to meet the needs of different application areas. This technology plays a significant role in the processing and refining of petroleum.
Pharmaceutical Industry: In the pharmaceutical industry, chlorination is utilized in the synthesis of drug molecules, especially when synthesizing chlorine-containing groups. The introduction of these chlorine-containing groups can alter the biological activity and pharmacological properties of drug molecules, leading to the development of new medications with therapeutic effects. Therefore, chlorination holds an irreplaceable position in the pharmaceutical field.
Textile Printing and Dyeing Industry: The textile printing and dyeing industry also extensively employs chlorination. Through chlorination treatment, dyes and auxiliaries required for dyeing and printing can be prepared. These dyes and auxiliaries exhibit excellent dyeing performance and printing effects, providing strong support for the diversification of textiles.
Pesticide and Fertilizer Production: Chlorination also plays a vital role in the production of pesticides and fertilizers. Through chlorination reactions, compounds with insecticidal, bactericidal, or growth-promoting functions can be synthesized. These compounds play a crucial role in agricultural production, contributing to increased crop yields and improved quality.
Technical Directions
Countries and regions such as the United States, the European Union, China, and Japan recommend prioritizing the use of continuous equipment (such as microchannel reactors) for chlorination reaction processes to meet the inherent safety requirements of each country.
Country/Region | Regulatory/Technical Document | Key Requirements |
United States | Guidelines from the Center for Chemical Process Safety (CCPS) | Recommends replacing batch processes with continuous flow reactors to reduce chlorine storage and runaway reaction risks. |
| Best Practices by the American Chemistry Council (ACC) | Mandates automated temperature/pressure controls and emergency shutdown systems (e.g., microchannel reactor technology) for chlorination reactors. |
European Union | Best Available Techniques Reference Document (BREF) | Prioritizes continuous production systems (e.g., tubular reactors) to mitigate intermediate accumulation hazards. |
| Technical Guidance by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | Emphasizes automated control systems for precise chlorine dosing and exothermic reaction management. |
China | Notice on Promoting Advanced Technologies like Microreactors (MIIT) | Encourages continuous-flow microreactors to enhance safety and efficiency in chlorination processes. |
| Safety Control Design Standards for Hazardous Chemical Processes (AQ/T 3034) | Requires automated temperature-pressure interlock controls and real-time chlorine flow monitoring systems. |
Japan | High-Pressure Gas Safety Act | Mandates fully enclosed pipeline transfer between chlorine storage tanks and reactors, prohibiting manual operations. |
| Chemical Process Safety Guidelines (METI) | Advises modular continuous reaction equipment for precise control and reduced human intervention. |
Case
PMG assisted a client in optimizing the reaction process for organic chlorine pesticides, which faced major challenges such as gas-liquid reactions, high heat release, multiple chlorinations, and corrosion. By adopting a continuous-flow reaction approach, PMG precisely configured equipment such as gas-liquid reactors, precise chlorine feed systems for controlled chlorine delivery, and gas-liquid separators. The optimized process achieved an annual production capacity of 20,000 tons, with stable operation of the equipment and good process flexibility. The main indicators were comparable to those of the current tank-based process. However, the optimized process demonstrated significant advantages in terms of process safety and production efficiency.
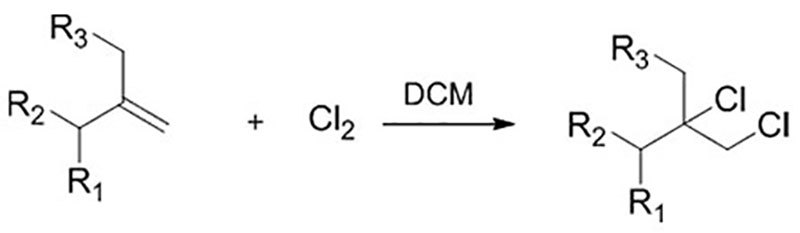
Reaction Equation
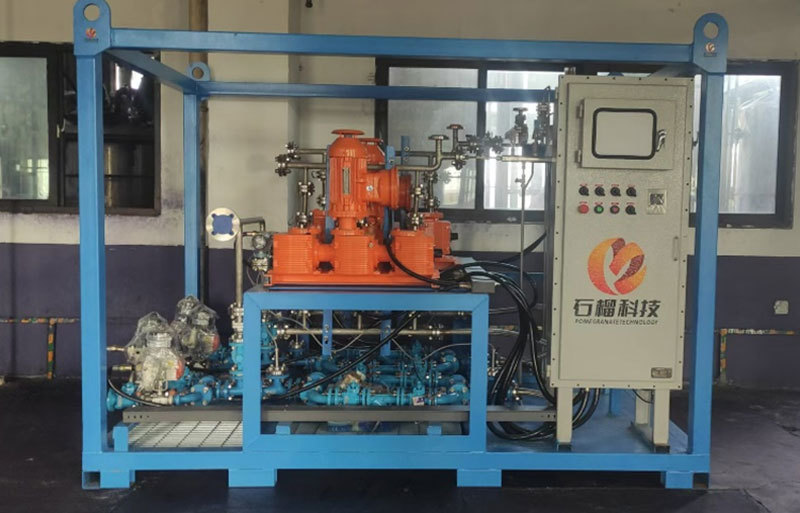

On-site Skid-mounted Equipment
Comparison of Production Efficiency Data
| Item | Reactor | MIC Reactor |
| Personnel Required | 6 | 3 |
| Footprint | 180m² | 12m² |
| Efficiency | 12 Hours | 10 Minutes |
| Continuity | Batch | Continuous |
| Safety | Spraying Phenomenon | High |
| Equipment Price | Low | Slightly Lower |
| Characteristics | High Pollution, Low Efficiency | High Efficiency, Continuous, Safe |
Previous page
Next page
Other News

