Application
Contact Us
Phone
Address
No. 60, Yungjing East Road, Liyuan Town, Tongzhou District, Beijing City, China
Oxidation
Category:
Application
Oxidation processes refer to chemical reactions in which substances interact with oxidizing agents (such as oxygen, ozone, peroxides, etc.), typically involving the transfer of electrons or the incorporation of oxygen atoms, leading to the oxidation of the substance. In industrial applications, oxidation reactions are widely used for producing chemicals (e.g., organic acids, alcohols, ketones, epoxides), energy conversion (e.g., combustion), wastewater treatment, or surface modification of materials.
Oxidation reactions are often exothermic. If cooling systems fail or stirring is uneven, accumulated heat may trigger uncontrolled chain reactions, even resulting in explosions. Many oxidation reactions (e.g., ammonia oxidation for nitric acid production) require high-temperature and high-pressure conditions. Overpressure in equipment or localized overheating can cause container ruptures or splattering of materials. Combustible gases (e.g., hydrogen) or liquid vapors in the reaction system may form explosive mixtures with air when reaching their explosive limits, posing significant explosion risks.
Regulatory Requirements
In China, regulations explicitly mandate key regulatory oversight of oxidation processes, requiring the use of continuous reaction devices. In Europe and the U.S., industry guidelines (e.g., CCPS, ECHA) promote the adoption of continuous reactors, while Japan, led by industry associations, advocates continuous processes to enhance safety.
| Country/Region | Regulation/Standard Name | Specific Requirements | Equipment Type |
| United States | OSHA 29 CFR 1910.119(j)(4) | Automated control systems (temperature, pressure control) | High-temperature oxidation reaction equipment (e.g., combustion furnaces) requiring explosion-proof pressure relief and temperature monitoring. |
| European Union | Seveso III Directive Annex II, Section 1.4 | Continuous process as a BAT (Best Available Techniques) option | Recommended continuous reaction processes to reduce hazardous material inventory and accident scale. |
| China | List of Key Regulated Hazardous Chemical Processes (Ministry of Emergency Management) | Mandatory continuous and automated processes | Priority use of continuous and automated reaction devices (e.g., microchannel reactors) to minimize human operational errors. |
| Japan | Industrial Safety and Health Act Article 28 | Automated or remote control devices | Continuous reactors recommended by the Japan Chemical Industry Association (JCIA) guidelines to reduce thermal runaway risks. |
Case
PMG assisted the client in completing the continuous production process design for the pesticide intermediate methyl p-toluenesulfonate, utilizing a gas-liquid continuous reaction to achieve a product purity of 99.5%.
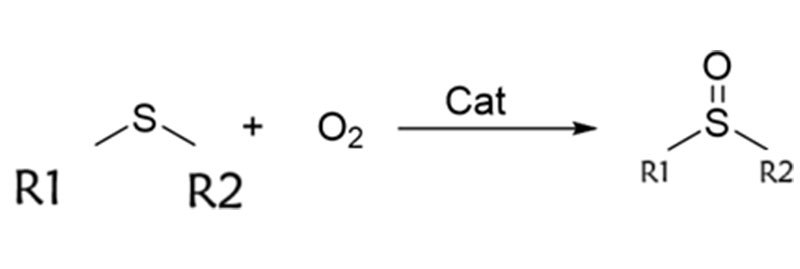
Reaction Equation
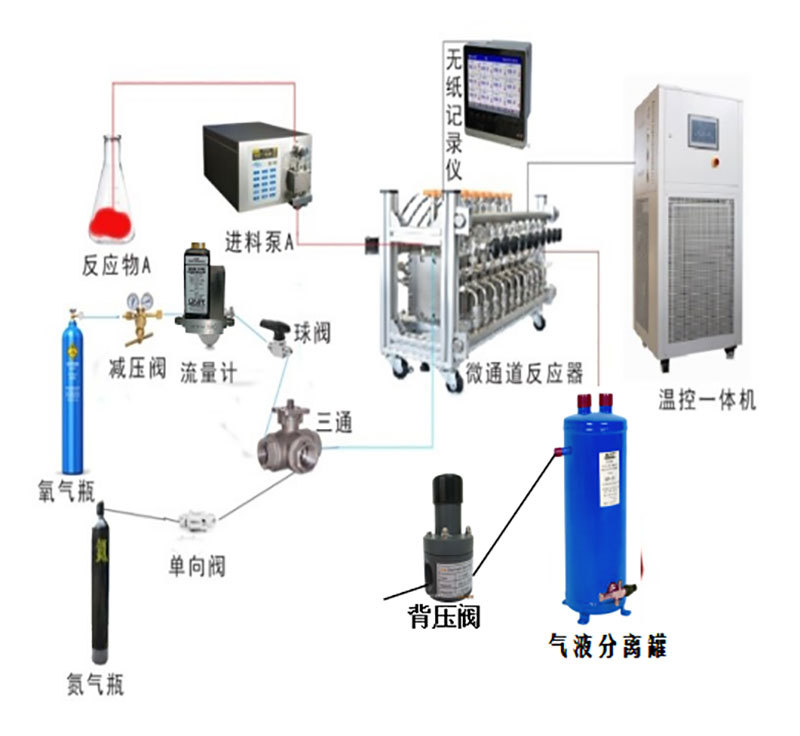

Industrial Equipment
Previous page
Next page
Other News

